Structural Formula
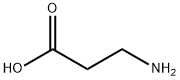
Endogenous β-amino acid, nonselective glycine receptor agonist, G-protein coupled orphan receptor (TGR7, MrgD) ligand. By supporting the osmotic stability of marine organisms, β-amino acid efflux acts as a cell protector.
Structural Formula
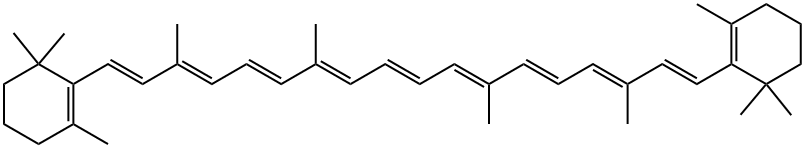
β-carotene (β-carotene) belongs to carotenoids. It is ubiquitous in nature and is the most stable natural pigment. It is an orange-yellow fat-soluble compound, shiny rhombohedral Chemicalbook or crystalline powder , mainly derived from natural foods such as green plants and yellow and orange fruits. The dilute solution of β-carotene is orange-yellow to yellow, orange when the concentration increases, and may be slightly red due to the polarity of the solvent.
Structural Formula

Collagen, also known as collagen, is the main component of the extracellular matrix, mainly in the form of insoluble fibrin. It is widely present in the bones, tendons, muscle sheaths, ligaments, sarcolemma, cartilage and skin of animals. It is an extremely important protein in connective tissue, accounting for 25% to 30% of the total protein in animals. The function of supporting organs and protecting the body is also the most important functional protein that composes the intercellular substance.
Structural Formula
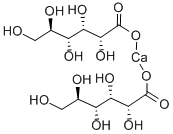
As a food additive, used as a buffer; curing agent; chelating agent; nutritional supplement. According to the “Hygienic Standards for the Use of Food Nutrition Fortifiers” (1993) promulgated by the Ministry of Health of my country, it can be used in cereals and their products, beverages, and the dosage is 18-38 grams, kg. 2. As a drug, it can reduce the permeability of capillaries, increase the degree of compactness, maintain the normal excitability of nerves and muscles, strengthen myocardial contractility, and help bone formation. It is suitable for allergic diseases, such as urticaria; eczema; skin pruritus; contact dermatitis, and serum sickness; angioedema as an adjuvant treatment. It is also suitable for convulsions and magnesium poisoning caused by hypocalcemia. It is also used to prevent and treat calcium deficiency.
Structural Formula
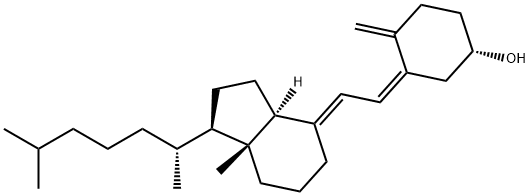
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that has been proven to be the true active form of vitamin D in the body. There are at least 10 known vitamin D, but the most important are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D Chemicalbook3 (cholecalciferol). Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3, is the most important form of vitamin D family. It mainly regulates the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body. Vitamin D3 is transformed from 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin by ultraviolet radiation.
Structural Formula
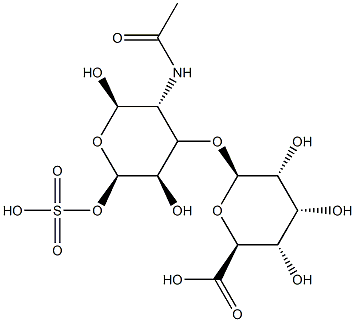
Chondroitin sulfate (chondroitinsulfate, CS) is an acidic mucopolysaccharide extracted and purified from animal cartilage tissue. Chondroitin sulfate has different structures such as A, C, D, E, H, and K. Chondroitin sulfate in nature mostly exists in soft bones, throat bones, nasal bones (41% in pigs), cattle, and horse diaphragms. and trachea (36% to 39%), and other tissues such as leg bones, ligaments, skin, and cornea. The content in fish cartilage is very rich, such as shark bone contains 50% to 60%, and the content in connective tissue is very small.
Structural Formula
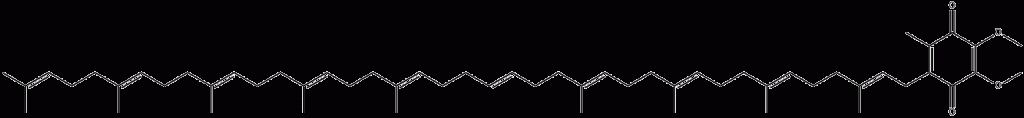
Coenzyme Q10 is a small molecule fat-soluble quinone organic compound widely present in animal and plant cells. Its structure is similar to that of vitamin K. Used alone or in combination with vitamin E, it is a strong antioxidant. Necessary to drive the body’s energy production (ATP) cycle. It has the function of promoting oxidative phosphorylation reaction and protecting the integrity of biofilm structure. Coenzyme Q from different sources has different numbers of isopentene units in its side chain. Humans and mammals have 10 isopentene units, so it is called coenzyme Q10. Coenzyme Q plays an important role in proton translocation and electron transfer in the respiratory chain in the body. It is an activator of cell respiration and cell metabolism, as well as an important antioxidant and non-specific immune enhancer.
Structural Formula
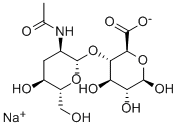
Hyaluronic acid is an acidic mucopolysaccharide, with its unique molecular structure and physical and chemical properties, it shows a variety of important physiological functions in the body, such as lubricating joints, regulating the permeability of blood vessel walls, regulating proteins, hydrolysis and detoxification Diffusion and operation, promote wound healing, etc. More importantly, hyaluronic acid has a special water-retaining effect, and is the most moisturizing substance found in nature so far, and is known as an ideal natural moisturizing factor.
Structural Formula
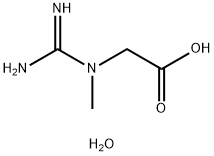
Creatine in the human body is formed from amino acids during a chemical process in the liver, and then sent from the blood to muscle cells where it is converted into creatine. The movement of human muscles provides energy by decomposing adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Creatine can automatically adjust the water entering the muscle, expand the cross-sectional muscle of the muscle, and increase the explosive power of the muscle.
Structural Formula
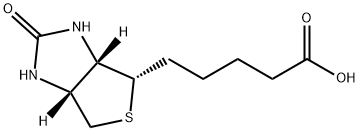
D Biotin is the eight form of the water-soluble vitamin, biotin, also known as vitamin B7. It is a coenzyme – or auxiliary enzyme – used in many metabolic reactions in the body. D Chemicalbook – Biotin is involved in lipid and protein metabolism, helping to convert food into glucose, which the body can use for energy. It is also important for maintaining the skin, hair and mucous membranes.
Structural Formula
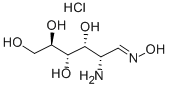
D-glucosamine hydrochloride (also known as glucosamine hydrochloride) is a drug for the treatment of bone and joint diseases and an antibiotic synergist. It is also a sweetener and antioxidant for food, and can also be used as a nutritional supplement for diabetics. It can also inhibit the growth of cancer cells and is the main raw material for the synthesis of new anticancer drug chlorurecin. Glucosamine hydrochloride and its derivatives have broad application prospects in medicine, light industrial cosmetics and other fields.
Structural Formula
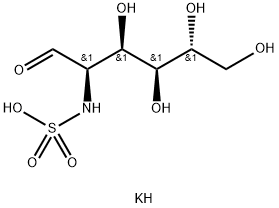
Glucosamine sulfate potassium salt is used together with chondroitin sulfate, which can have a good analgesic effect, and it has also been verified in the application that it has no side effects. It can play a very good role in the treatment of bone and joint diseases, and the effect is also very significant. Acupuncture Chemicalbook is good for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. At the same time, it is also more suitable for people who have joint pain and frequent back pain to relieve symptoms, and can also treat sciatica. It also has a certain effect on osteoporosis.
Structural Formula
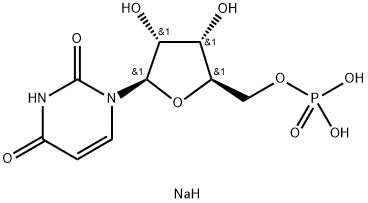
Disodium uridine is also called disodium 5′-uridine, which can be used as an important intermediate in the production of nucleic acid drugs, health food and biochemical reagents. It is also used in the manufacture of uridine diphosphate glucose, uridine triphosphate, polyadenylic acid and other drugs, and plays an important role in the treatment of many major diseases.
Structural Formula
chemical properties
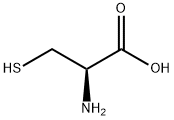
Colorless crystalline substance; slight odor, sour taste; easily soluble in water, acetic acid, ammonia water and ethanol, insoluble in ether, benzene, acetone, ethyl acetate, carbon disulfide and carbon tetrachloride; in neutral or It is easily oxidized to cystine in slightly alkaline solution, trace iron and heavy metal ions can promote oxidation, and can exist stably in acid.
Structural Formula

Chitosan (chitosan, CS), also known as deacetylated chitin, is obtained by deacetylation of chitin, the second largest resource-rich natural polymer in the world. Generally, chitosan with a degree of deacetylation greater than 70% is called chitosan. At present, chitin is an underutilized resource, and its marine biological reserves alone account for 30% of the total discarded shells of aquatic products, up to several million tons, so the resources of chitin and chitosan are very rich.
Structural Formula
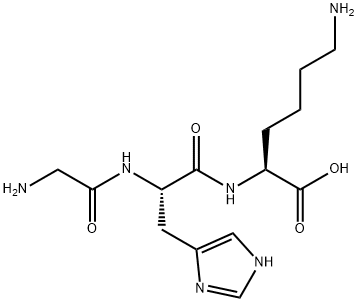
Tripeptide (copper peptide) is formed by three amino acids, tripeptide is also called blue copper peptide; glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. Tripeptide is a triplet molecule composed of three amino acids Chemicalbook and two peptide bonds, which can effectively prevent the nerve conduction of a substance called acetylcholine, relax muscles, and improve dynamic wrinkles.
Structural Formula
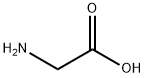
Glycine is the simplest one among the 20 members of the amino acid series. It is also called aminoacetic acid. It is an amino acid not necessary for the human body. It has high solubility in solvents, is basically insoluble in non-polar solvents, and has high boiling and melting points. Glycine can exhibit different molecular forms by adjusting the acidity and alkalinity of the aqueous solution. The side bond of glycine is a hydrogen atom. Since its alpha carbon also has a hydrogen atom, glycine is not optically isomerizable. Due to the very small side bonds of glycine, it can occupy spaces that other amino acids cannot, for example as an amino acid within the collagen helix. It is white crystal or light yellow crystalline Chemicalbook powder at room temperature. It has a unique sweet taste, which can ease the acid and alkali taste, cover the bitter taste of saccharin added in food and enhance the sweet taste. If the human body consumes too much glycine, not only will it not be absorbed and utilized by the human body, but it will also break the body’s absorption balance of amino acids and affect the absorption of other amino acids, resulting in nutritional imbalance and affecting health. Milk-containing beverages produced with glycine as the main raw material are likely to have adverse effects on the normal growth and development of adolescents and children. Density 1.1607. Melting point 232~236°C (decomposition). Soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol and ether. It can react with hydrochloric acid to form hydrochloride. It exists in the tendons of dry low-grade cargo. It can be formed by the action of monochloroacetic acid and ammonium hydroxide, and can also be obtained by hydrolyzing and refining gelatin.
Structural Formula
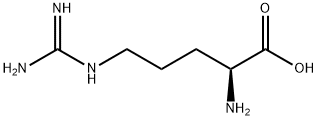
L-Arginine is an encoded amino acid in protein synthesis and is one of the eight essential amino acids for the human body. The body needs it for many functions. For example, it stimulates the body to release certain chemicals such as insulin and human growth hormone. This amino acid also helps remove ammonia from the body and promotes wound healing. The body also needs it to produce sarcosine. Nitric oxide is produced when L-arginine is decomposed, so it can dilate blood vessels and increase blood flow. Under normal circumstances, the body itself can produce enough L-arginine. But when it is insufficient, it can be supplemented by eating foods rich in arginine. L-arginine can be found in any food that contains protein such as meat, poultry, cheese products, fish, etc. Arginine-rich foods include almonds, walnuts, dried sunflower kernels, dark chocolate, chickpeas, melons, peanuts, raw lentils, hazelnuts, Brazil nuts, red meat (in moderation), cashews, salmon, pistachios Fruits, soybeans and walnuts.
Structural Formula
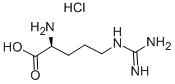
White or nearly white almost odorless crystalline powder. It melts and decomposes at about 235°C. Stable in dry state. The pH of a 3% aqueous solution is about 5.7. Soluble in water (90%, 25 ℃). Slightly soluble in hot ethanol, insoluble in ether.
Structural Formula
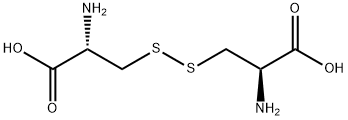
L-cystine has a wide range of uses: 1. Used in biochemical research. Prepare biological media. It is used in biochemical and nutritional research, and in medicine, it can promote the oxidation and reduction of cells in the body, increase white blood cells and prevent the development of pathogenic bacteria. Mainly used for various alopecia. It is also used for dysentery, typhoid fever, influenza and other acute infectious diseases, asthma, neuralgia, eczema and various poisoning diseases, etc., and has the effect of maintaining the configuration of Chemicalbook protein. Also used as a food flavoring agent. 2. Biochemical reagents for the preparation of biological culture medium. It is also an important component of amino acid infusion and compound amino acid preparation. 3. As a feed nutrition enhancer, it is beneficial to animal development, increasing body weight, liver and kidney functions, and improving fur quality. 4. It can be used as a cosmetic additive, which can promote wound healing, prevent skin allergies and treat eczema.
Structural Formula
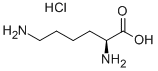
L-Lysine is one of the eight essential amino acids in the human body, which can promote human development, enhance immune function, and improve the function of central nervous tissue. Brain protective agent for treating craniocerebral trauma, chronic brain tissue ischemia and hypoxic diseases.
Structural Formula
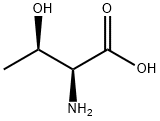
Threonine is produced by W. C. Rose, which was isolated and identified from fibrin hydrolyzate in 1935, has been proved to be the last essential amino acid discovered. It is the second or third limiting amino acid of livestock and poultry, and it has extremely important physiological functions in animals. Such as promoting growth, improving immune function, etc.; balancing dietary amino acids, making the ratio of amino acids closer to ideal protein, and reducing the requirements of livestock and poultry for protein content in feed. Lack of threonine can lead to symptoms such as reduced animal feed intake, stunted growth, decreased feed utilization, and suppressed immune function. In recent years, synthetic products of lysine and methionine have been widely used in feed, and threonine has gradually become a limiting factor affecting animal production performance. Further research on threonine will help effectively guide livestock and poultry production.
Structural Formula
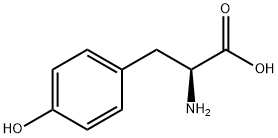
Tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid, which is a raw material for various products in the body. Tyrosine can be converted into various physiological substances through different metabolic pathways in the body, such as dopamine, adrenaline, thyroxine, melanin and opium poppy (opium). ) of papaverine. These substances are closely related to the control of nerve conduction and metabolic regulation. Studying tyrosine metabolism helps to understand the pathological process of certain diseases. For example, alkapsis is related to tyrosine metabolism disorder in Chemicalbook, the lack of alkaptic acid oxidase in the body of the patient causes the metabolite of tyrosine, alkaptic acid, to be unable to continue to decompose, and it is excreted from the urine and oxidized into a black substance in the air. The diapers of sick children will gradually turn black when exposed to the air, and the urine will also turn black after a long time. Albinism is also related to the metabolism of tyrosine. Patients lack tyrosinase so that the tyrosine metabolite 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine cannot form melanin, so the hair and skin are white.
Structural Formula
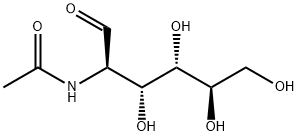
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine is the basic unit of many important polysaccharides in biological cells, especially the exoskeleton of crustaceans has the highest content. It is an important precursor for the synthesis of bifidus factors and has many important physiological functions in organisms.
Structural Formula
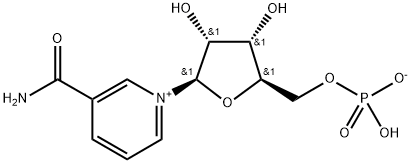
Nicotinamide mononucleotide, also known as β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), is the synthetic substrate of coenzyme I, and NMN is also used in anti-aging research. Studies have shown that β-NMN can also regulate the secretion of insulin and affect the expression level of mRNA. β-NMN has broad application prospects in the field of medical treatment. β-Nicotinamide mononucleoside Chemicalbook acid is the product and key NAD+ intermediate of the extracellular nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (eNAMPT) reaction. It improves glucose tolerance by restoring NAD+ levels in HFD-induced T2D mice. It also enhanced hepatic insulin sensitivity and restored gene expression related to oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and circadian rhythms, in part through SIRT1 activation.
Structural Formula
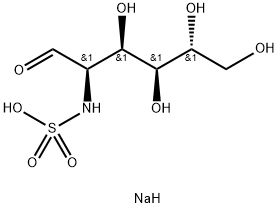
Glucosamine sulfate sodium salt, also known as 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose sulfate sodium chloride compound salt, is a drug for the treatment and prevention of osteoarthritis.
Structural Formula

The raw materials for making fish oil preparations are commonly found in mackerel, herring, tuna, flounder, salmon, cod liver, whale blubber, seal oil, etc. Generally, a small amount of vitamin E is added to play an antioxidant role. Fish oil is a new resource food in my country. In a broad sense, fish oil is the fat of fish including cod liver oil, but the main functional components of fish oil generally referred to are DHA (diChemicalbook docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid). enoic acid), has the effect of regulating blood lipids, and the main functional components of cod liver oil are vitamin A and vitamin D, the main function is to prevent and treat vitamin A and vitamin D deficiency. Infants under 1 year of age do not require fish oil supplementation if they are adequately fed breast milk or formula + complementary foods (vitamin D supplementation may be considered)
Structural Formula
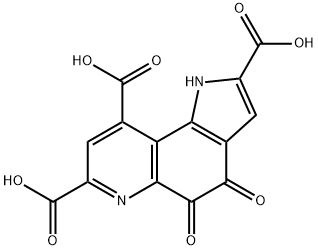
The scientific name of PQQ is pyrroloquinoline quinone, which is a new prosthetic group that can treat heart disease, neurological diseases, protect the liver, and maintain mitochondrial functions. Pyrroloquinoline quinone is widely found in prokaryotes, plants and mammals. It is not only the prosthetic group of many enzymes, it is responsible for the function of transferring electrons, protons and chemical groups in enzymatic reactions, and can also stimulate The growth of microorganisms, the germination of plant pollen, and the promotion of plant growth.
Structural Formula
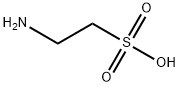
Taurine, also known as β-aminoethanesulfonic acid, was first isolated from bezoar, hence the name. Appearance is colorless or white oblique crystals, odorless, stable chemical properties, soluble in organic solvents such as ether, Chemicalbook is a sulfur-containing non-protein amino acid, exists in a free state in the body, and does not participate in the biosynthesis of proteins in the body. Although taurine does not participate in protein synthesis, it is closely related to the metabolism of cystine and cysteine.
Structural Formula
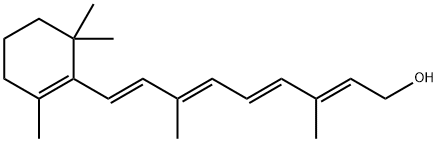
Retinol is a fat-soluble vitamin, which exists in animal foods in the form of free aldehydes or esters, and is rich in fat, protein, milk, and liver. Plants do not contain vitamin A, but contain the precursor of vitamin A (provitaminA), which exists in vegetables such as carrots and tomatoes, and can be converted into vitamin A after being absorbed by animals and animals. Retinol is necessary to maintain human growth, development, reproduction and the stability of cell membranes, and plays an important role in the process of vision. Retinal is replenished and consumed due to continuous metabolism in the body, and it needs to be supplemented by oxidized vitamin A in time. Vitamin A is related to the normal structure and function of the upper and lower cells. When it is deficient, it will cause dryness and inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea, and even blindness. Slow and so on. Vitamin A oil as a nutritional supplement is fatty oil or its concentrate obtained from the liver and pylorus of aquatic animals. Crush the fresh fish liver and pylorus, add 1-2% sodium hydroxide solution to pH8-9. Retinol can be used in sausage, margarine, bread, dairy products, fruit juice powder, peanut butter, etc.
Structural Formula
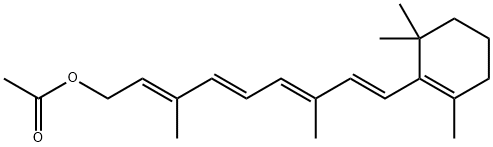
Vitamin A acetate is a fat-soluble vitamin, which is a VitaminA nutritional supplement. Vitamin A participates in various physiological processes of the human body. When Vitamin A is insufficient in the body, it will lead to impaired rod cell function, anemia, decreased immune function, poor growth, etc. Therefore, Vitamin A nutritionally fortified foods are widely used in many countries. Vitamin A acetate is an unsaturated ester, oily, easy to oxidize, soluble in fat or organic solvents, but insoluble in water, so it is difficult to add it evenly in food, so its application range is limited. After microencapsulation , can improve its water solubility and stability, and its state changes from oily to powdery, which is convenient for storage, transportation and advanced processing.
Structural Formula
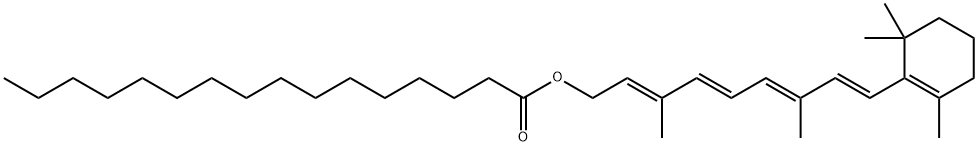
Retinyl palmitate (retinylpalmitate) is a type of vitamin A (VitaminA). It is a chemicalbook ester of retinol and palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid that is the main component of palm oil. Retinyl Palmitate is easily absorbed by the skin and converted to Retinol. It is a yellow or yellow-red solid or oily substance.
Structural Formula
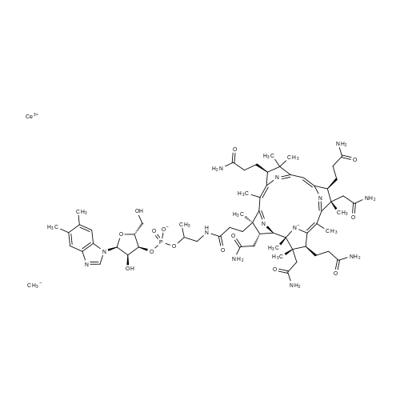
Methylcobalamin is a drug for the treatment of peripheral nerve disorders. Compared with other vitamin B12 preparations, it has good transmissibility to nerve tissue. It can promote nucleic acid-protein-lipid metabolism through methyl conversion reaction and repair damaged nerve tissue. It plays the role of coenzyme in the process of synthesizing methionine from homocysteine, especially participates in the synthesis of thymidine from deoxyuridine nucleoside, and promotes the synthesis of DNA and RNA. In addition, in the experiment of glial cells, the drug increases the activity of methionine synthase and promotes the synthesis of myelin lipid lecithin. Improve the metabolic disorder of nervous tissue, promote the synthesis of axon and its protein, make the transport speed of bone protein close to normal, and maintain the function of axon.
Structural Formula
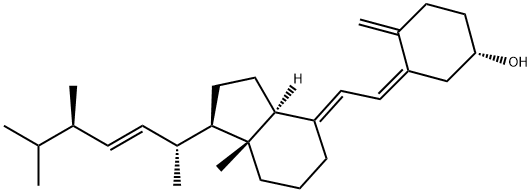
There are at least 10 known types of vitamin D, but the most important are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferaldehyde). Vitamin D2 is produced from ergosterol in UV-irradiated plants Chemicalbook, but there are very few stocks in nature. Vitamin D3 is transformed from 7-dehydrocholesterol contained in the human epidermis and dermis by ultraviolet radiation in sunlight. The safety of vitamin D2 is better than that of vitamin D3.
